Cat. #160729
A2780 PTX(4) resistant cell line
Cat. #: 160729
Sub-type: Continuous
Unit size: 1x10^6 cells / vial
Availability: 8-10 weeks
Organism: Human
Tissue: Ovary
Disease: Cancer
Model: Tumour line
£575.00
This fee is applicable only for non-profit organisations. If you are a for-profit organisation or a researcher working on commercially-sponsored academic research, you will need to contact our licensing team for a commercial use license.
Contributor
Inventor: Jolanta Szenajch ; Luiza Handschuh ; Aleksandra Świercz ; Michał Góralski ; Alicja Szabelska-Beręsewicz; Joanna Zyprych-Walczak ; Idzi Siatkowski
Institute: Military Institute of Medicine - National Research Institute
Tool Details
*FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY (for other uses, please contact the licensing team)
- Name: A2780 PTX(4) resistant cell line
- Cancer type: Ovarian cancer
- Cancers detailed: Ovarian
- Research fields: Cancer;Drug development
- Tool sub type: Continuous
- Parental cell: A2780
- Organism: Human
- Tissue: Ovary
- Disease: Cancer
- Growth properties: Adherent
- Model: Tumour line
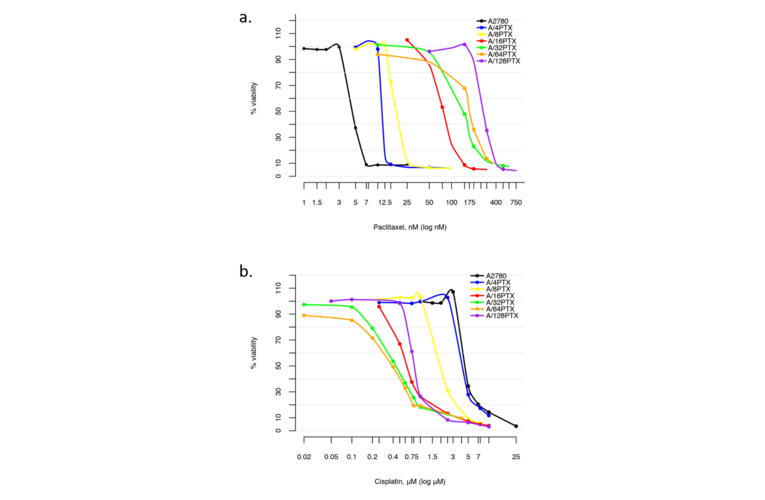
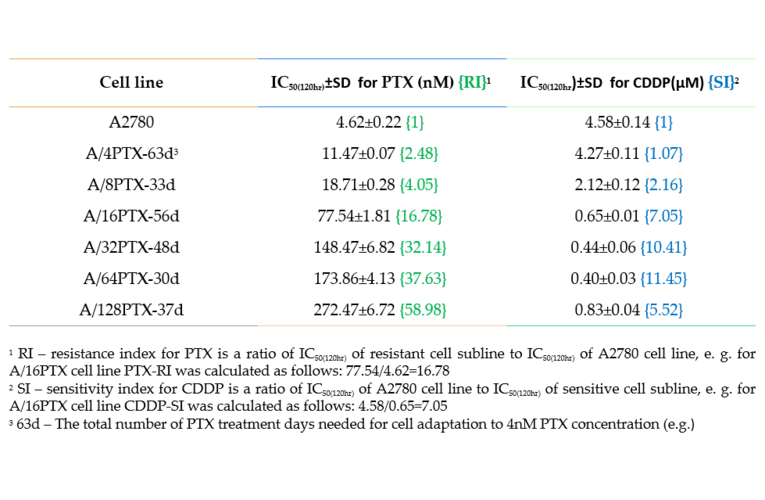
- Description: The paclitaxel (PTX) resistant A2780 PTX (4) cell line with collateral sensitivity to cisplatin (CDDP) (inverse resistance) has been developed by continuous growing of A2780 parental cell line (cat. no 152706) in step-wise increases of PTX doses (0.25 nM - 0.5 nM - 1 nM- 2 nM - 4 nM; for details see Fig. 1). The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) for PTX is about twice as high the IC50 for A2780, whereas for CDDP it remains unchanged (for details see Tab. 1). PTX and CDDP are standard chemotherapeutic drugs used in the treatment of ovarian cancer and acquired resistance to them remains a major obstacle in therapy. The trend of developing the inverse resistance is dominant in clinical practice, therefore A2780 PTX (4) cell line with other sublines of the series (see Notes for details) can be used as a primary tool for deciphering the molecular and cellular mechanisms of drug resistance in ovarian cancer. This cell line was generated as part of a series of isogenic ovarian cancer lines with gradually changing inverse resistance to PTX (resistant) and CDDP (sensitive); see A2780 PTX (8) Cat no:160730, A2780 PTX (16) Cat no:160731, A2780 PTX (32) Cat no:160732, A2780 PTX (64) Cat no:160733, and A2780 PTX (128) Cat no:160734 for the others (see Tab. 1 and Fig. 2 for details). Transcriptomes of six sublines were sequenced and the mRNA dataset was deposited under Gene Expression Omnibus Accession No GSE159791.Patent number: 233178
- Production details: Split sub-confluent cultures (70-80%) seeding at 4 x 1000 (tolerated range: 1 x 1000 to 1 x 10 0000) cells/cm2 preferably using cell dissociation solution (CDS: 0.3g Na2EDTA, 8 g NaCl, 0.56 g sodium bicarbonate, 1 g D-glucose and 0.4 g KCl per 1000 ml H2O; filter sterilized) or TrypLE ExpressTM, 5% CO2, 37oC. Culture cells without drug until they have been fully adhered (after 24 h).
Target Details
- Target: Paclitaxel resistance
Applications
- Application notes: This cell line was generated as part of a series of isogenic ovarian cancer lines with gradually changing inverse resistance to PTX (resistant) and CDDP (sensitive); see A2780 PTX (8) Cat no:160730, A2780 PTX (16) Cat no:160731, A2780 PTX (32) Cat no:160732, A2780 PTX (64) Cat no:160733, and A2780 PTX (128) Cat no:160734 for the others (see Tab. 1 and Fig. 2 for details). Transcriptomes of six sublines were sequenced and the mRNA dataset was deposited under Gene Expression Omnibus Accession ...
Handling
- Format: Frozen
- Growth medium: RPMI 1640 medium + 2mM L-alanine-L-glutamine (GlutaMAXTM) + 5% heat-inactivated Foetal Bovine Serum (FBS) , at 37?°C and 5% CO2 . To keep the stability of resistance profile not using antibiotics and antimycotics is recommended. Cells should be cultured without PTX (up to 10 days) to avoid the resistance escalation. After this time the maintenance treatment with 4 nM PTX for one passage is recommended.
- Unit size: 1x10^6 cells / vial
- Shipping conditions: Dry ice
References
- Szenajch et al. 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21(23): 9218. PMID: 33287223